-
 Jun , 12 2025
Jun , 12 2025
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄), commonly referred to as LFP, has emerged as a preeminent cathode material in the realm of lithium-ion batteries, distinguished by its unparalleled safety profile, environmental compatibility, and robust electrochemical performance. The material's intrinsic stability stems from its olivine-type crystal structure, which provides a stable framework for lithium-ion in...
View More
-
 Jun , 19 2025
Jun , 19 2025
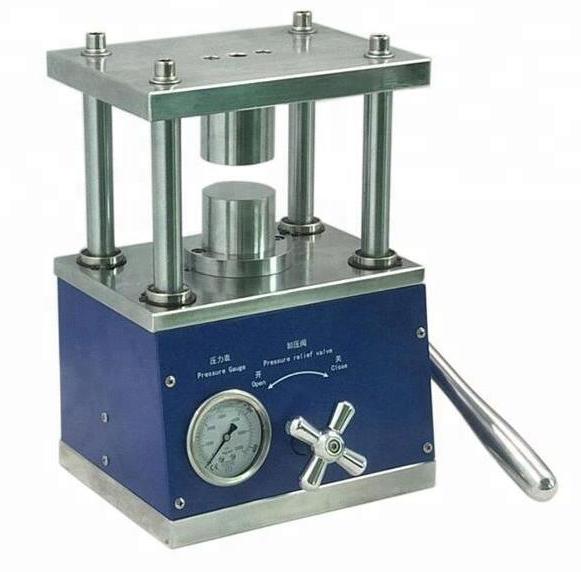
In the field of battery research and development, the laboratory battery powder press machine stands as a cornerstone instrument, pivotal for fabricating battery electrodes and prototypes. Widely used in fields such as powder metallurgy, cement, catalysis, silicon hydrochloric acid, batteries, ceramics, and universities for component analysis. Powder is compressed into test pieces and adapted to v...
View More
-
 Jul , 24 2025
Jul , 24 2025
In the race to decarbonize transportation and energy systems, battery electrolytes—a crucial but often overlooked component—are emerging as a linchpin of innovation. These ionic conductors, which enable lithium-ion movement between electrodes, are undergoing rapid transformation to address safety, energy density, and cost challenges. From smart thermoresponsive solutions to solid-state breakthroug...
View More
-
 Aug , 21 2025
Aug , 21 2025
Structural Advantages and Energy Storage Potential of NVP NVP Na3V2(PO4)3 powder belongs to the family of sodium superionic conductor (NASICON) materials, and its unique crystal structure endows it with a host of excellent properties. The framework of the NASICON structure forms stable sodium accommodation sites, while its open three-dimensional ion transport channels facilitate the rapid intercal...
View More
-
 Sep , 04 2025
Sep , 04 2025
Mesocarbon Microspheres (MCMB) are micrometer sized spherical carbon materials with a nematic liquid crystal layered stacking structure generated by thermal condensation of heavy aromatic compounds such as asphalt. Some MCMBs are prepared using petroleum asphalt or coal tar as raw materials. Structure and Characteristics The outstanding performance of MCMB is entirely due to its unique physic...
View More
-
 Oct , 31 2025
Oct , 31 2025
Binders are the unsung heroes of battery electrode fabrication—though they typically account for just 2–5 wt% of an electrode’s total mass, their impact on battery performance, stability, and scalability is profound. In battery laboratories, researchers rely on a diverse range of binders to address the unique challenges of emerging electrode materials (e.g., silicon, sulfur, sodium-based compounds...
View More
-
 Nov , 28 2025
Nov , 28 2025
Since its isolation in 2004, graphene—a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice—has revolutionized materials science with its extraordinary properties: exceptional electrical conductivity (10⁴–10⁵ S/m, 100x higher than copper), ultra-high specific surface area (2630 m²/g), superior mechanical strength (130 GPa), and excellent thermal stability. These attributes make it a game-...
View More
-
 Dec , 05 2025
Dec , 05 2025
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for large-scale energy storage and low-cost portable electronics, thanks to sodium’s abundant reserves, low cost, and similar electrochemical behavior to lithium. However, SIBs face critical challenges: the larger ionic radius of Na⁺ (1.02 Å vs. Li⁺’s 0.76 Å) leads to slower ion diffu...
View More
-
 Dec , 19 2025
Dec , 19 2025
This is a battery grade high-purity chemical precursor. Lithium oxide (Li2O) is a white powder, mainly designed for synthesizing various lithium based solid electrolytes, and is one of the core materials for developing the next generation of solid-state batteries. Lithium oxide (Li2O) is highly hygroscopic and quickly reacts with moisture in the air to form lithium hydroxide (LiOH). This...
View More
 Jun , 12 2025
Jun , 12 2025
 Jun , 19 2025
Jun , 19 2025
 Jul , 24 2025
Jul , 24 2025
 Aug , 21 2025
Aug , 21 2025
 Sep , 04 2025
Sep , 04 2025
 Oct , 31 2025
Oct , 31 2025
 Nov , 28 2025
Nov , 28 2025
 Dec , 05 2025
Dec , 05 2025
 Dec , 19 2025
Dec , 19 2025