-
 Oct , 23 2025
Oct , 23 2025
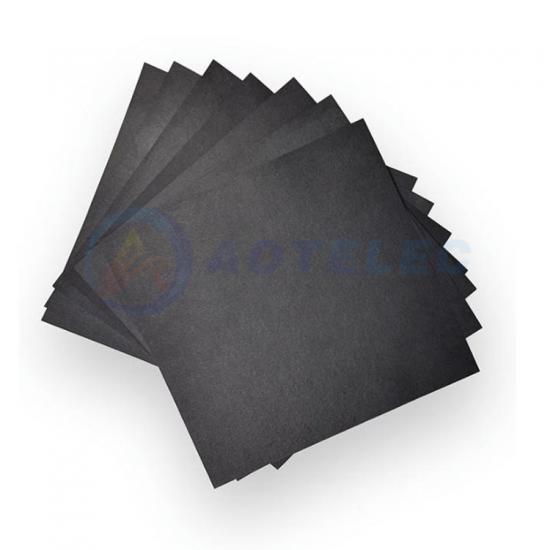
Carbon paper—often referred to as carbon fiber paper (CFP) or porous carbon substrate—has emerged as a critical material in modern battery systems, thanks to its unique combination of high electrical conductivity, structural flexibility, porous architecture, and chemical stability. Unlike traditional paper, carbon paper is manufactured from carbon fibers (typically polyacrylonitrile-based or pitch...
View More
-
 Oct , 31 2025
Oct , 31 2025
Binders are the unsung heroes of battery electrode fabrication—though they typically account for just 2–5 wt% of an electrode’s total mass, their impact on battery performance, stability, and scalability is profound. In battery laboratories, researchers rely on a diverse range of binders to address the unique challenges of emerging electrode materials (e.g., silicon, sulfur, sodium-based compounds...
View More
-
 Nov , 21 2025
Nov , 21 2025
1. Introduction In the lithium-ion battery manufacturing process, the mixing quality of electrode pastes directly affects the electrochemical performance and cycle stability of the battery. Meanwhile, the mixing uniformity of functional materials such as ceramic materials is crucial for their subsequent application effects. Traditional mixing equipment tends to entrap air during operation, resulti...
View More
-
 Nov , 28 2025
Nov , 28 2025
Since its isolation in 2004, graphene—a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice—has revolutionized materials science with its extraordinary properties: exceptional electrical conductivity (10⁴–10⁵ S/m, 100x higher than copper), ultra-high specific surface area (2630 m²/g), superior mechanical strength (130 GPa), and excellent thermal stability. These attributes make it a game-...
View More
-
 Dec , 05 2025
Dec , 05 2025
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as one of the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) for large-scale energy storage and low-cost portable electronics, thanks to sodium’s abundant reserves, low cost, and similar electrochemical behavior to lithium. However, SIBs face critical challenges: the larger ionic radius of Na⁺ (1.02 Å vs. Li⁺’s 0.76 Å) leads to slower ion diffu...
View More
-
 Dec , 19 2025
Dec , 19 2025
This is a battery grade high-purity chemical precursor. Lithium oxide (Li2O) is a white powder, mainly designed for synthesizing various lithium based solid electrolytes, and is one of the core materials for developing the next generation of solid-state batteries. Lithium oxide (Li2O) is highly hygroscopic and quickly reacts with moisture in the air to form lithium hydroxide (LiOH). This...
View More
-
 Jan , 23 2026
Jan , 23 2026
Amid the accelerating iteration of the global new energy industry, lithium batteries, as the core power carrier in fields such as new energy vehicles and energy storage systems, have attracted widespread attention for their performance improvement and industrial upgrading. Among the core components of lithium batteries, electrode current collector materials directly determine the battery's energy ...
View More
 Oct , 23 2025
Oct , 23 2025
 Oct , 31 2025
Oct , 31 2025
 Nov , 21 2025
Nov , 21 2025
 Nov , 28 2025
Nov , 28 2025
 Dec , 05 2025
Dec , 05 2025
 Dec , 19 2025
Dec , 19 2025
 Jan , 23 2026
Jan , 23 2026